Medical experts are alerting doctors and the public about a highly contagious and rare fungal strain following the first reported case of sexually transmitted ringworm in the U.S.
“Healthcare providers should be aware that Trichophyton mentagrophytes type VII is the newest addition to a group of severe skin infections now present in the United States,” stated Dr. Avrom Caplan, a dermatologist at New York University Grossman School of Medicine, in a university news release.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Trichophyton mentagrophytes type VII is a sexually transmitted fungus.
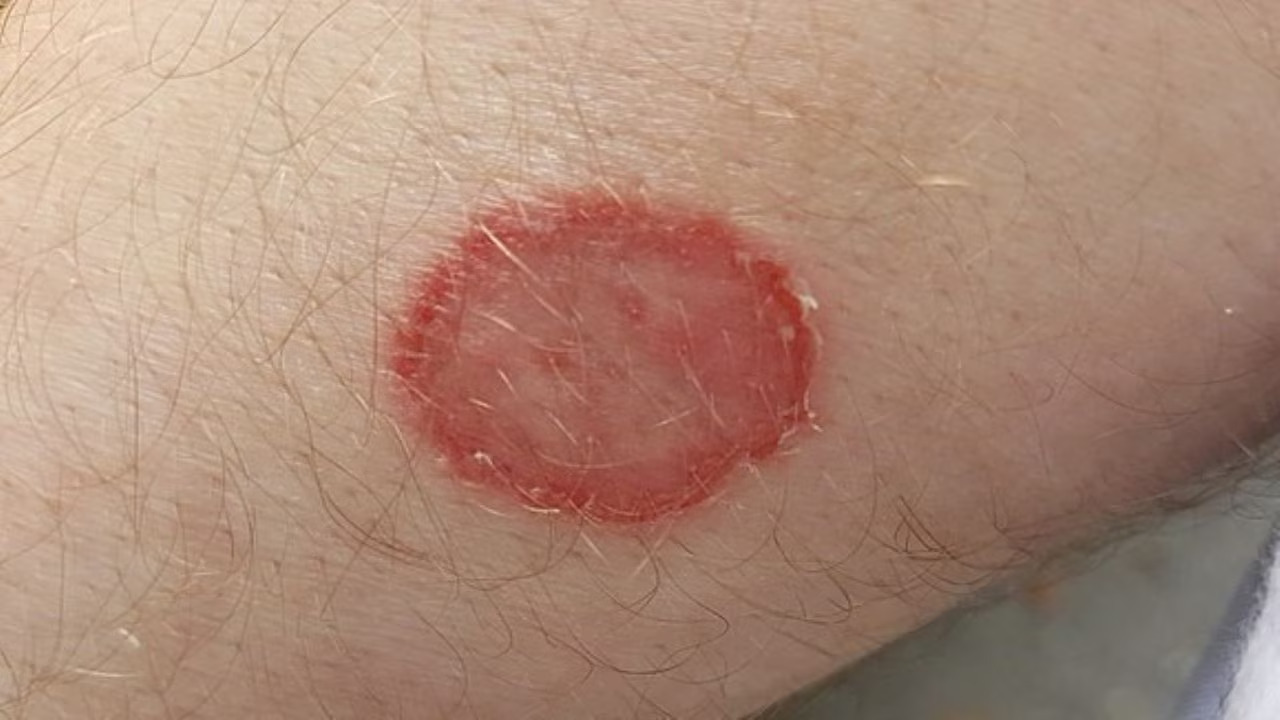
A new report in JAMA Dermatology, released Wednesday, describes the first case in the U.S.: a man in his 30s from New York City developed ringworm (tinea) on his genitals, buttocks, and limbs after engaging in sexual activities with men during trips to California, England, and Greece.
Upon returning home, the man developed an itchy red rash on his groin, genitals, and buttocks. Tests confirmed he had contracted the rare fungus.
What is Trichophyton mentagrophytes type VII?
Trichophyton mentagrophytes type VII is a drug-resistant fungus that causes skin disease in both animals and humans and is transmitted through sexual contact, according to the CDC.
The CDC reports cases of this fungus worldwide, particularly among men who have sex with men and travelers who developed genital ringworm after visiting Southeast Asia.
Dr. Caplan noted in the report that the rash might resemble an eczema flare rather than the typical circular pattern of a ringworm infection. Although not fatal, the infection can cause permanent scarring.
Dr. Caplan previously identified the first two cases of a different drug-resistant ringworm infection last year, caused by Trichophyton indotineae. These infections, while not sexually transmitted, are highly contagious and drug-resistant.
Since then, Caplan’s team at NYU Langone Health has detected 11 cases of Trichophyton indotineae ringworm in New York City.
Report: An Emerging Public Threat
The 11 ringworm cases in New York caused by Trichophyton indotineae have been linked to travel to Asia, according to a report published in the same journal in May. Medical professionals noted these cases are resistant to standard therapies, including first-line antifungals.
The report highlights the fungus as an emerging public health threat because it causes ringworm infections that can sometimes be unresponsive to terbinafine, a first-line oral antifungal.
According to the Mayo Clinic, terbinafine is a prescription tablet used to treat fungal infections of the scalp and body, fingernails, toenails, jock itch, and athlete’s foot.
Symptoms of Trichophyton mentagrophytes type VII
Symptoms of Trichophyton mentagrophytes type VII include:
- Intense itching
- Inflamed circular patterns on the skin
- Hair and nail issues
- Causes athlete’s foot